$\require{color}$
这玩意把人绕晕了都。
1、是否为氧化还原反应的判定
置换反应一定是,因为那个单质一定在反应过程中发生了化合价变化;
复分解反应一定不是,因为复分解反应中不会有化合价变化(这是初中知识)(此条存疑,详见百度百科-氧化还原反应-复分解反应);
分解反应和化合反应,看情况。
2、氧化与还原的判定
比如这个:
$\begin{matrix}
\textcolor{red}0 & \textcolor{blue}0 & 点燃 & \textcolor{red}{+4}\textcolor{blue}{-2}\\
\textcolor{red}C & +\textcolor{blue}O_2&===&\textcolor{red}{C}\textcolor{blue}{O}_2
\end{matrix}$
初中知识告诉我们,这是氧化反应。
再比如这个:
$\begin{matrix}
\textcolor{red}{+2}&\textcolor{blue}0&高温&\textcolor{red}0&\textcolor{blue}{+4}\\
2\textcolor{red}{Cu}O&+\textcolor{blue}C&===&2\textcolor{red}{Cu}&+\textcolor{blue}CO_2
\end{matrix}$
初中知识告诉我们,这是还原反应。
事实上,到了高中,这俩就合并成“氧化还原反应”了。
因此,对于第 1 个反应,我们可以发现:
| 元素 | $C$ | $O$ |
|---|---|---|
| 化合价变化 | 升高 | 降低 |
| 电子 | 失去 | 得到 |
| 自己被? | 氧化 | 还原 |
| 扮演的角色 | 还原剂 | 氧化剂 |
对于第 2 个反应,我们可以发现:
| 元素 | $C$ | $Cu$ |
|---|---|---|
| 化合价变化 | 升高 | 降低 |
| 电子 | 失去 | 得到 |
| 自己被? | 氧化 | 还原 |
| 扮演的角色 | 还原剂 | 氧化剂 |
总结:
化合价升高的元素则为还原剂,自身被氧化;化合价降低的元素则为氧化剂,自身被还原;
有氧化,必有还原;有化合价升高,必有化合价降低;有电子失去,必有电子得到。
或者说,氧化剂具有氧化性,在氧化别的元素的同时自己被还原;还原剂具有还原性,在还原别的元素的同时自己被氧化。
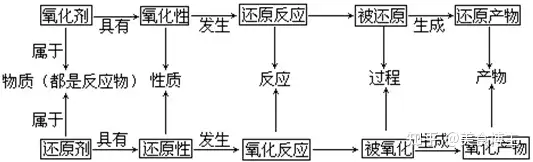
如果实在记不住,那就在考场上,在草稿纸上写一写吧。
3、氧化剂、还原剂、氧化产物、还原产物
还是回到那个方程式:
$\begin{matrix}
\textcolor{red}{+2}&\textcolor{blue}0&高温&\textcolor{red}0&\textcolor{blue}{+4}\\
2\textcolor{red}{Cu}O&+\textcolor{blue}C&===&2\textcolor{red}{Cu}&+\textcolor{blue}CO_2
\end{matrix}$
作为氧化剂的元素或离子,经过还原反应后,会变成还原产物。
作为还原剂的元素或离子,经过氧化反应后,会变成氧化产物。
部分物质同时具有氧化性和还原性。
还原剂的还原性大于还原产物,氧化剂的氧化性大于氧化产物。
好绕啊……
好,来道题看看。
已知下列反应:$Cl_2+2NaBr===2NaCl+Br_2$,$2KI+Br_2===2KBr+I_2$,$Na_2S+I_2===2NaI+S\downarrow$。
则:
(1)$Cl^-$、$Br^-$、$I^-$、$S^{2-}$ 的还原性由强到弱排序?
(2)$Cl_2$、$Br_2$、$I_2$、$S$ 的氧化性由强到弱排序?
首先,给关键的元素或离子标上化合价。
然后,判断哪个是还原剂,哪个是氧化剂,哪个是还原产物,哪个是氧化产物。
| 化学方程式 | 还原剂 | 氧化剂 | 还原产物 | 氧化产物 | 以上都不是 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| $\begin{matrix}\textcolor{red}0&\textcolor{green}{+1}\textcolor{blue}{-1}&&\textcolor{green}{+1}\textcolor{red}{-1}&\textcolor{blue}0\\\textcolor{red}{Cl}_2&+2\textcolor{green}{Na}\textcolor{blue}{Br}&===&2\textcolor{green}{Na}\textcolor{red}{Cl}&+\textcolor{blue}{Br}_2\end{matrix}$ | $Br^-$ | $Cl_2$ | $Cl^-$ | $Br^2$ | $Na$ |
| $\begin{matrix}\textcolor{green}{+1}\textcolor{blue}{-1}&\textcolor{red}0&&\textcolor{green}{+1}\textcolor{red}{-1}&\textcolor{blue}0\\2\textcolor{green}{K}\textcolor{blue}{I}&+\textcolor{red}{Br}_2&===&2\textcolor{green}{K}\textcolor{red}{Br}&+\textcolor{blue}{I}_2\end{matrix}$ | $I^-$ | $Br_2$ | $Br^-$ | $I_2$ | $K$ |
| $\begin{matrix}\textcolor{green}{+1}\textcolor{blue}{-2}&\textcolor{red}0&&\textcolor{green}{+1}\textcolor{red}{-1}&\textcolor{blue}0\\\textcolor{green}{Na}_2\textcolor{blue}{S}&+\textcolor{red}{I}_2&===&2\textcolor{green}{Na}\textcolor{red}{I}&+\textcolor{blue}{S}\downarrow\end{matrix}$ | $S^{2-}$ | $I^2$ | $I^-$ | $S$ | $Na$ |
最后,根据前面提到的:
还原剂的还原性大于还原产物,氧化剂的氧化性大于氧化产物。
最终得出答案。
(1)$S^{2-}>I^->Br^->Cl^-$
(2)$Cl_2>Br_2>I_2>S$
链接阅读
花絮
这么一条方程式:$\begin{matrix}\textcolor{red}0&\textcolor{green}{+1}\textcolor{blue}{-1}&&\textcolor{green}{+1}\textcolor{red}{-1}&\textcolor{blue}0\\\textcolor{red}{Cl}_2&+2\textcolor{green}{Na}\textcolor{blue}{Br}&===&2\textcolor{green}{Na}\textcolor{red}{Cl}&+\textcolor{blue}{Br}_2\end{matrix}$
大概这么长:
\begin{matrix}
\textcolor{red}0&\textcolor{green}{+1}\textcolor{blue}{-1}&&\textcolor{green}{+1}\textcolor{red}{-1}&\textcolor{blue}0\\\\
\textcolor{red}{Cl}_2&+2\textcolor{green}{Na}\textcolor{blue}{Br}&===&2\textcolor{green}{Na}\textcolor{red}{Cl}&+\textcolor{blue}{Br}_2
\end{matrix}
